Silicone Cup Manufacturing and Quality Control
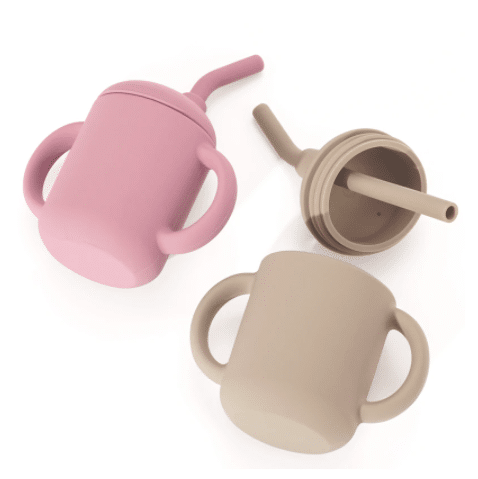
Silicone cups have gained significant popularity in recent years, and it’s easy to see why. These versatile and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional cups offer a range of benefits that make them an excellent choice for both hot and cold beverages. Consumers have very clear expectations for silicone cups: leak-proof, odor-free, dust-free, easy to clean, high-temperature resistant, drop-resistant, non-sticky after prolonged use, non-whitening, colorfast, and non-yellowing. However, from a B2B perspective (brand owners/distributors/purchasers), the risks associated with silicone cups are more concentrated:
Compliance: Food contact materials (FCM) standards differ significantly from those for children’s products, leading to substantial market discrepancies;
Process stability: Silicone molding, vulcanization, post-vulcanization, and surface treatment all determine the final odor, volatile organic compounds, and performance;
Sealing and assembly: Common leak-proof structures in silicone cups (valve, sealing ring, spout, straw) have extremely stringent requirements for size, hardness, and resilience;
User reputation: Negative reviews on social media and e-commerce platforms heavily focus on “odor, leakage, blackening of the straw, difficulty in cleaning, and taste/odor migration.”
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what makes silicone cups stand out and the various advantages they offer,and how to control the quality of silicone cups.
What are Silicone Cups?
Silicone cups are reusable containers made from a high-quality, food-grade silicone material. Silicone, a synthetic rubber-like material, is known for its flexibility, durability, and heat resistance. It’s commonly used in a wide array of applications, from kitchen utensils to medical devices, and has become increasingly popular in the production of drinkware. The silicone cup is subject to “high-frequency use + high-frequency cleaning + ingestion,” and a poor experience will result in an immediate negative review.Therefore, the manufacturing and quality control of silicone cups are of utmost importance.
Key Benefits of Silicone Cups
Manufacturing Processes for Silicone Cups
Silicone cups have gained popularity for their durability, safety, and versatility. Understanding the different manufacturing processes for producing silicone cups can help businesses and consumers make informed decisions when selecting the right product.
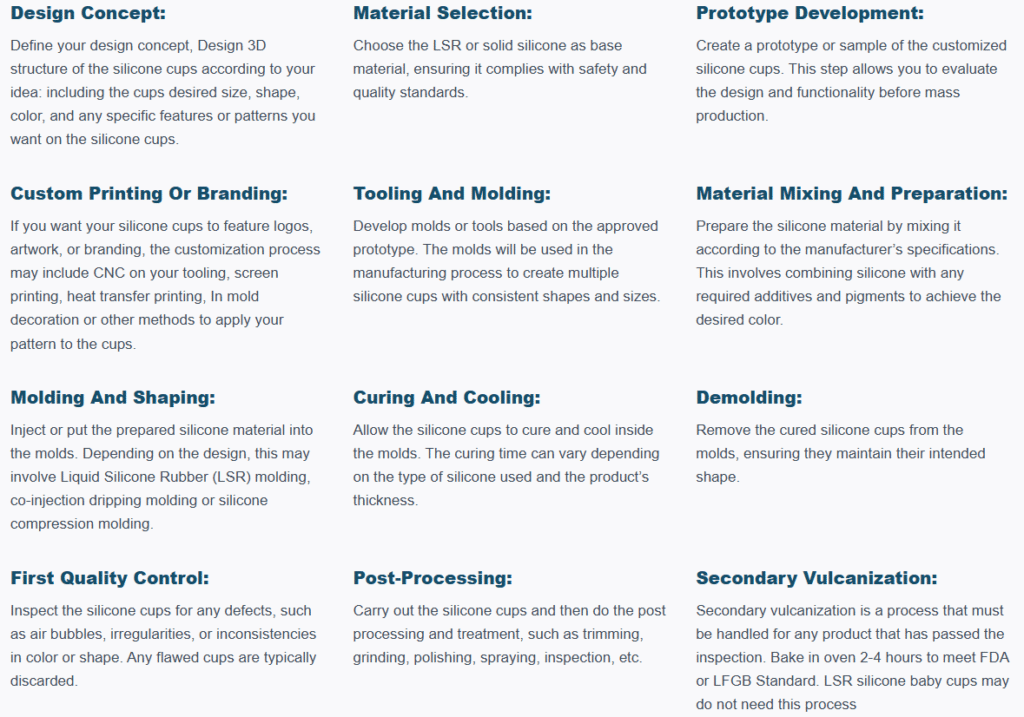

Overview of Silicone Production Methods
There are several methods for producing silicone products, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Some common production methods include:
- Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection molding
- High-consistency rubber (HCR) molding
- Compression molding
- Transfer molding
- Extrusion
The choice of production method depends on factors such as product complexity, production volume, and material properties. For silicone cups, LSR injection molding and HCR molding are the most commonly used methods.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding
LSR injection molding is a popular method for producing silicone products with complex shapes and fine details. It involves injecting a liquid silicone rubber mixture into a heated mold under high pressure. The mixture then cures and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold. This process allows for high precision and repeatability, making it ideal for large-scale production.
Advantages of LSR injection molding include
- High precision and consistency
- Fast cycle times and high production rates
- Minimal waste
- Suitable for complex designs
Further Reading: the difference between Injection molding VS Compression Molding in terms of the Definition, manufacturing process, materials used, production rates, cost, and application
High Consistency Rubber (HCR) Molding
HCR molding is another method for producing silicone cups, using a high-consistency rubber material that is more solid than liquid. The HCR material is placed into a mold, which is then heated and compressed, causing the silicone to cure and take the shape of the mold. HCR molding is particularly suited for small to medium production runs and simpler designs.
Advantages of HCR molding include:
- Lower equipment and tooling costs compared to LSR molding
- Easier to handle and process
- Suitable for small to medium production runs
Choosing the Right Process for Silicone Cup Production
When selecting the right manufacturing process for silicone cups, it is essential to consider factors such as production volume, product complexity, and budget. LSR injection molding is often preferred for large-scale production and complex designs, while HCR molding may be more suitable for smaller production runs and simpler shapes.
By understanding the different manufacturing processes available, businesses and consumers can make informed decisions when selecting silicone cups that meet their specific requirements and preferences.
The information provided above offers just a brief overview of silicone production methods. If you’re interested in learning more about the technical aspects and details, please check out our Molding Service introduction for a deeper understanding.
How to control the quality of silicone cups?
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
Raw material batch COA, mixing records, color batch management
Key physical properties: hardness, tensile strength, tear strength (especially high tear resistance is required at the nozzle root)
Compliance documentation chain:
Common US benchmark: 21 CFR 177.2600 (Extraction Restriction and Reusable Rubber Product Requirements)
EU: FCM framework requirements + GMP (EC 2023/2006)
Molding Process Control (IPQC)
First Article Confirmation: Dimensions, weight, appearance, parting line, venting marks, shrinkage/flow marks
Process Parameter Locking: Mold temperature, vulcanization time, injection speed/pressure (LSR), demolding method
Random Edge Control: Random edges not only affect appearance but also the adhesion of sealing surfaces, leading to micro-leakage
C. Post-Processing and Cleaning Control (Most easily overlooked, but most impactful on reputation)
Post-vulcanization conditions documented (temperature/time/loading)
Cleaning water and drying control (avoiding water stains and secondary contamination)
Packaging Environment: Cardboard box odor and oil stains will “cumulate” onto the silicone.
- Tensile and tear strength testing
- Compression set testing
Heat resistance and thermal stability testing - Chemical resistance testing
- Food safety testing, such as FDA and LFGB compliance
These tests help ensure that silicone cups meet performance, durability, and safety requirements, providing consumers with confidence in their purchase.
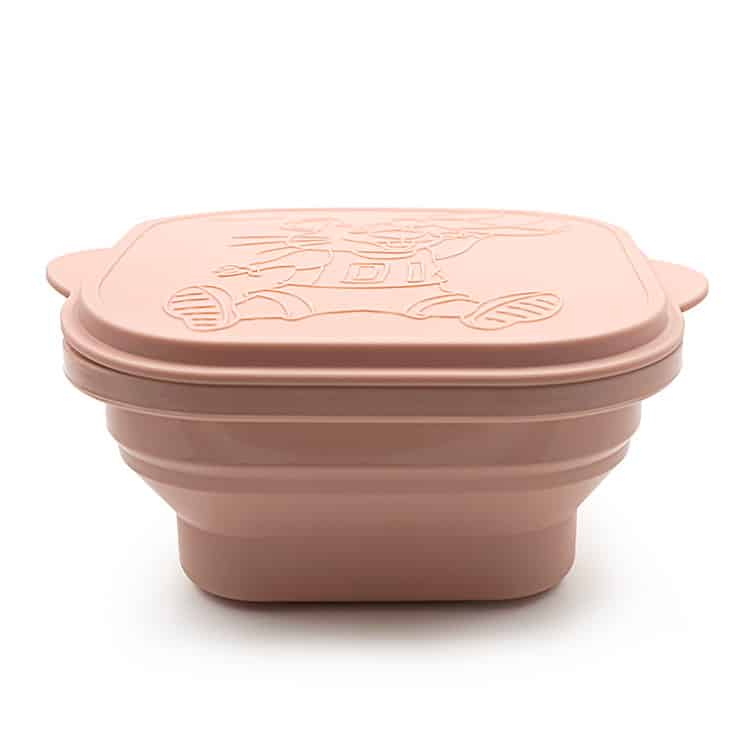
Design Considerations for Silicone Cups
When designing silicone cups, it’s crucial to strike a balance between functionality and aesthetics. While the primary focus should be on ensuring the cup is practical, easy to use, and durable, the visual appeal should also be considered to create an attractive product that consumers will enjoy using.
Designing collapsible and non-collapsible cups involves different considerations, such as:
For collapsible cups:
- Ensuring easy and secure folding
- Maintaining structural integrity when expanded
- Providing a leak-proof seal when collapsed
For non-collapsible cups:
- Ensuring durability and stability
- Providing comfortable grip and insulation
- Meeting size and volume requirements
When designing silicone cups, it’s essential to consider the target audience’s needs and preferences, such as:
- Size and capacity
- Ease of use and cleaning
- Portability and storage
- Color and style options
- Compatibility with accessories, such as lids or sleeves
By considering these factors, designers can create silicone cups that cater to various consumer preferences and demands. Check Our Custom Services
Who Cares about Silicone Cup Manufacturing and Quality Control?
Infant and Toddler Brands / DTC Brands: “Low customer complaints + compliant documentation + consistent colors across the entire series.”
Channel/Retail Procurement: “Stable supply, controllable delivery time, low risk of failing random inspections.”
Gift/IP Collaboration Partners: “High-end appearance, accurate color reproduction, confidentiality, and rapid prototyping.”
How to clean silicone cups?
Daily Cleaning: Warm water + neutral detergent + soft sponge; avoid strong friction with steel wool, especially on printed/painted areas.
Dishwasher: Upper rack recommended; thoroughly dry after washing before storage to reduce odor and water stains.
Straw/Valve: Detachable structure recommended with cleaning brush; remind users that “residue from high-sugar drinks can easily breed odors.”
FAQ For silicone cups?
1) Q: What compliance requirements are there for silicone cups?
A: The common approach is—in the US, compliance with 21 CFR 177.2600 (Extraction Requirements for Reusable Rubber in Food Contact Articles); in the EU, adherence to the food contact materials framework requirements and GMP production; in the German market, many brands refer to BfR recommendations (including XV Silicones).
2) Q: How to choose between LSR and HCR solid silicone?
A: LSR is more suitable for high consistency, multi-cavity automation, and small sealing parts; HCR molding is also commonly used for thick walls or specific textures. Ultimately, it depends on your structure, production volume, and consistency requirements.
3) Q: Why do some batches of the same cup leak?
A: This is usually due to critical dimension drift, burrs, hardness fluctuations, or unstable assembly positioning. It is recommended to perform SPC on critical dimensions and standardize leakage testing.
4) Q: How to reduce “odor negative reviews”? A: Incorporate post-curing/washing/drying/packaging odor control into GMP documentation management, and conduct sensory sampling and sample retention for traceability.
5) Q: What additional attention should be paid to toddler training cups?
A: In addition to food contact, structural safety, information labeling, and mechanical and physical testing can refer to the framework of EN 14350.
6) Q: Can silicone cups be dishwasher safe?
A: Most age-appropriate cup designs consider ease of cleaning, but long-term dishwasher resistance depends on the material system, structure, and process verification. It is recommended that brands use “dishwasher cycle leakage retest + sensory retest” to provide a more reliable statement.
7) Q: Why do new silicone cups have an odor/develop an odor after prolonged use?
A: Common reasons include insufficient curing, residual volatiles, and cross-contamination of odors from packaging and the environment.
S: Implement stable post-curing and washing/drying processes, and document them within the GMP framework;
Conduct sensory sampling and sample retention for traceability;
Implement “odor control” for packaging materials and the storage environment.
8) Q: Why does silicone sealant leak (leakage when inverted, leaks when shaken, leaks even after tightening)?
A: Common causes: Dimensional drift of the sealing surface, burrs, unstable hardness, insufficient valve structure rebound.
S: SPC for critical dimensions, 100% visual inspection of the sealing surface;
Hardness windows for valves/sealing rings and positioning with assembly fixtures;
Standardized online leakage testing (posture + pressure + time).
9) Q: Straws turn black/difficult to clean/have residue
A: Common causes: Non-removable structure, cleaning dead spots, beverage residue.
S: Design with detachable and visible channels;
Include a cleaning brush with the cup and include cleaning steps in the instruction manual (this will significantly reduce negative reviews).
10) Q: Deformation, whitening, surface dust
A: Common causes: Uneven wall thickness, unstable process windows, improper surface treatment or formula selection.
S: Optimize wall thickness uniformity and reinforcing ribs;
Establish DOE process windows for different colors/hardnesses;
Use “tactile feel/anti-sticking” as an engineering indicator (not just looking at the appearance).
Conclusion
Silicone cups offer a durable, safe, and versatile option for consumers seeking an alternative to traditional materials like plastic, glass, and ceramic. By understanding the various manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and design considerations, businesses and consumers can make informed decisions when selecting silicone cups that meet their specific needs and preferences. With a focus on safety, performance, and customer satisfaction, silicone cups will continue to gain popularity in the marketplace.